
PowerPoint Tips for Handling Multimedia Errors
Multimedia elements such as images, videos, and audio clips are often key components of a PowerPoint presentation, enhancing the overall message and engagement. However, multimedia errors can occur, disrupting your presentation and causing unnecessary stress. Whether it’s a missing video, a corrupt image, or an audio clip that won’t play, understanding how to troubleshoot and fix multimedia errors is essential for delivering a smooth and professional presentation.
In this blog, we’ll discuss common multimedia issues in PowerPoint and provide tips for handling them efficiently.
1. Images Not Displaying or Appearing Corrupt
One of the most frequent multimedia errors in PowerPoint involves images not displaying correctly. This may happen if an image is not embedded properly, or if the file is corrupt.
Solution:
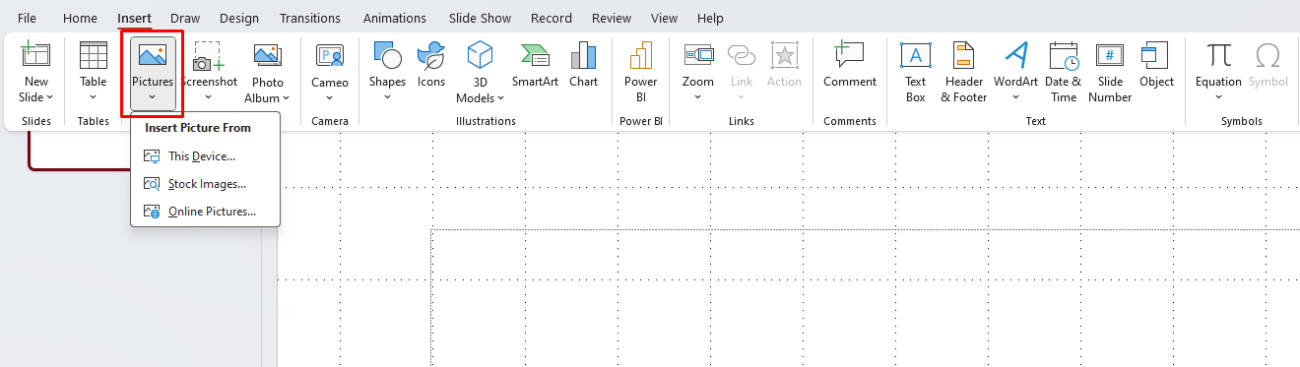
- Embed Images Properly: When adding images, always ensure they are fully embedded into the PowerPoint file rather than linked. If the image is linked, and the file path changes or the image is moved, it may not display correctly. To embed an image, use Insert > Pictures, and select the appropriate image from your device.
- Check for Corrupt Files: If an image appears corrupt, try opening the image in another program (like an image viewer) to ensure the file is intact. If it doesn’t open, the file is likely damaged, and you may need to replace it with a new version.
- Resize or Compress Large Images: Large image files can slow down PowerPoint and may not display properly. Consider resizing or compressing the image by going to Picture Tools > Format > Compress Pictures to reduce the file size.
2. Video Not Playing or Displaying a Black Screen
Videos can be an excellent addition to your presentation, but sometimes they won’t play or show up as a black screen. This issue is usually related to file compatibility, file corruption, or missing codecs.
Solution:
- Check Video Format: PowerPoint supports several video formats, but some may cause issues depending on the version you’re using. Formats like MP4 and WMV are widely supported and should work seamlessly. If your video is in a different format, consider converting it to MP4 or WMV using an online converter.
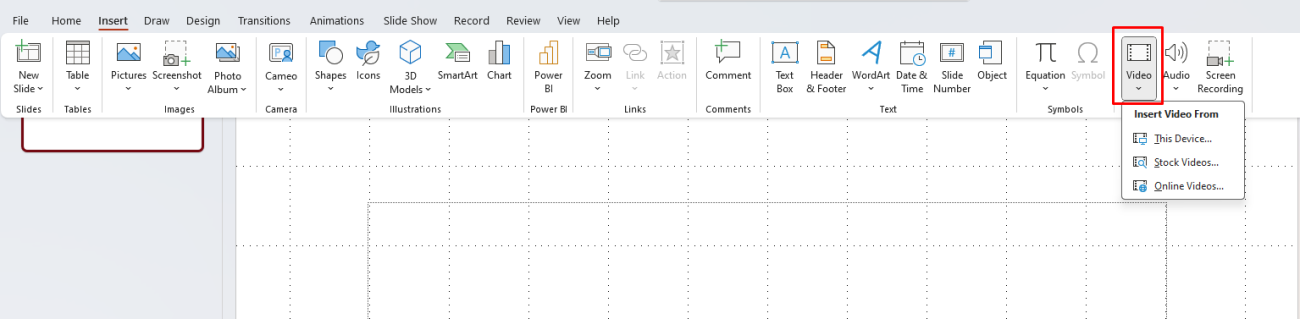
- Embed the Video: Similar to images, it’s best to embed videos in your presentation instead of linking them. To embed a video, select Insert > Video and choose to embed it from your device rather than linking to an external file.
- Update Video Drivers: If videos are still not playing, check if your video drivers are up to date. Outdated drivers can cause playback issues in PowerPoint.
- Disable Hardware Graphics Acceleration: Sometimes, hardware acceleration can cause video playback issues. To disable this feature, go to File > Options > Advanced, scroll down to the Display section, and check the box for Disable hardware graphics acceleration.
3. Audio Not Playing in Your Presentation
Audio files such as voiceovers or background music can greatly enhance a presentation, but audio issues are common, particularly if the file isn’t embedded correctly or is in an unsupported format.
Solution:
- Ensure Correct Audio File Format: PowerPoint supports MP3, WAV, and WMA formats. If your audio is in a different format, try converting it to one of these formats before inserting it into your presentation.
- Check Audio Settings: Ensure that your computer’s sound is not muted and that your audio device is functioning properly. In PowerPoint, right-click on the audio icon and select Playback. Ensure that Start is set to Automatically or On Click, depending on when you want the audio to play.
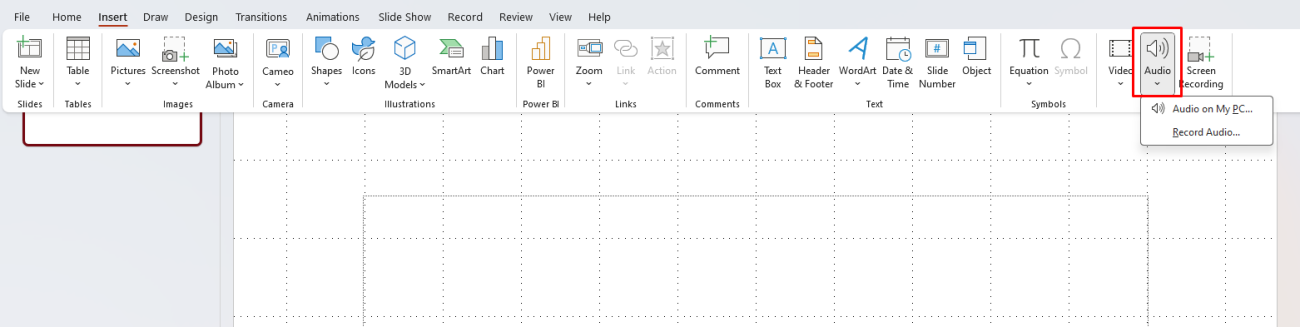
- Embed Audio Files: Just like with videos, embedding your audio file rather than linking it can prevent playback issues. To embed audio, go to Insert > Audio > Audio on my PC and select the file you want to insert.
4. Multimedia Files Won’t Play in Presentation Mode
Sometimes, multimedia elements may play fine in edit mode but fail to work during the actual presentation. This can be due to several factors, such as improper embedding or file path issues.
Solution:
- Test in Slideshow Mode: Always test your presentation in slideshow mode before your actual presentation. This will help you identify issues early and avoid surprises.
- Check File Paths: If you’re linking to external multimedia files (rather than embedding them), ensure that the file paths are correct. If you’re sharing your presentation with others or opening it on a different computer, make sure the linked files are accessible. It’s best to embed your files to avoid such issues.
- Reinsert Multimedia Files: If the problem persists, try removing and reinserting the multimedia files. Sometimes this refreshes the settings and resolves the issue.
5. Multimedia Files Don’t Appear After Transferring Files
If you transfer a PowerPoint presentation to a different device and find that multimedia files (like videos and images) are missing or don’t play, the problem may be related to file paths or missing files.
Solution:
- Package for Sharing: When you need to share your presentation with others or transfer it to another device, use PowerPoint’s Package for CD feature to ensure all multimedia files are included. This option can be found under File > Export > Package Presentation for CD. This will bundle the presentation and all associated multimedia files into one folder.
- Copy All Multimedia Files: Before transferring your presentation, make sure all linked multimedia files are in the same folder as the PowerPoint file. This ensures that when you move the file, everything stays intact.
- Save as PowerPoint Show: If you’re sending the presentation to someone else for viewing, save it as a PowerPoint Show file (.ppsx) to prevent any file path issues.
6. Embedded Videos or Audio Play in QuickTime or Other External Players
If you encounter a situation where embedded videos or audio play in an external player (like QuickTime) instead of within PowerPoint, it could be because the default media player is not set correctly.
Solution:
- Embed Video in PowerPoint Format: Instead of relying on external players, embed the video using PowerPoint’s supported video formats (MP4, WMV). This avoids the need for an external player and ensures compatibility.
- Use Windows Media Player or VLC for Audio/Video: If you prefer using external players for specific file types, ensure that your system’s default media player is set to one that PowerPoint supports (like Windows Media Player or VLC).
7. Broken Links to Online Multimedia
Inserting multimedia files from online sources can be convenient, but broken links or changes to the online source can cause these files to fail to appear in your presentation.
Solution:
- Download and Embed Files Locally: Rather than linking to online multimedia, download the files and embed them in your presentation to avoid the risk of broken links. This ensures the files will always be available, regardless of the internet connection or changes to the online source.
- Update or Fix Links: If you must use online sources, double-check the links to make sure they are still valid. If the link has changed, update it by going to Insert > Links and modifying the URL.
Looking for a reliable and affordable way to get Microsoft Office? Buy the cheapest Office keys today and unlock the full potential of your productivity tools!

