
How can you Check the System Performance in Windows?
Monitoring your computer’s performance is essential for maintaining its health and ensuring that it operates smoothly. Windows provides various tools and features to help you assess system performance effectively. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to check system performance in Windows.
1. Using Task Manager
One of the easiest ways to check system performance is through Task Manager. To access it:
- Press
Ctrl + Shift + Escor right-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager. - Click on the Performance tab. Here, you can see real-time data on CPU, memory, disk, and network usage.
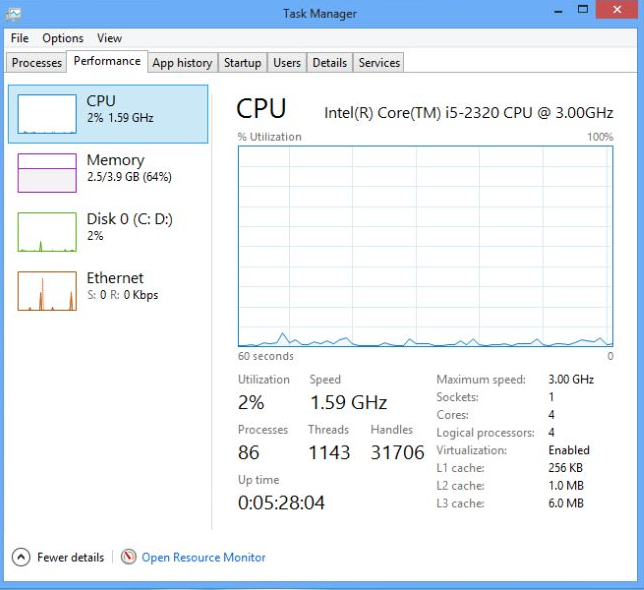
What to Look For:
- CPU Usage: High usage might indicate that applications are demanding too much from your processor.
- Memory Usage: If memory usage is consistently high, it may be time to upgrade your RAM or close some applications.
- Disk Activity: High disk usage could slow down your system. Investigate which processes are using the disk heavily.
2. Resource Monitor
For a more detailed analysis, you can use Resource Monitor, which is integrated into Windows.
- Open Task Manager and go to the Performance tab.
- At the bottom, click on Open Resource Monitor.
Resource Monitor provides detailed information about CPU, memory, disk, and network usage, along with specific processes that are consuming resources.
3. Windows Performance Monitor
For advanced users, Windows Performance Monitor is a powerful tool that allows for comprehensive system performance tracking.
- Press
Win + R, type perfmon, and hit Enter. - In Performance Monitor, you can add various counters to monitor specific metrics. Click on the green plus sign to add counters like processor time, memory, and more.
This tool also allows you to create data collector sets to log performance over time, which can be useful for identifying trends.
4. Using the System Assessment Tool
Windows includes a built-in tool called the Windows Experience Index, which assesses your system’s capabilities and provides a score.
- Open the Control Panel.
- Go to System and Security > System.
- Click on Windows Experience Index (if available) to see your system’s scores for CPU, RAM, and graphics.
5. Third-Party Applications
If you prefer more features or a user-friendly interface, consider third-party applications such as:
- HWMonitor: Monitors hardware performance and temperatures.
- CrystalDiskInfo: Provides detailed information about your hard drives and SSDs.
- MSI Afterburner: Primarily used for gaming, it can monitor CPU and GPU performance.
6. Checking for System Bottlenecks
While monitoring, keep an eye out for signs of performance bottlenecks, such as:
- Slow boot times: This can be an indication of software or hardware issues.
- Frequent crashes or freezes: These symptoms could point to hardware malfunctions or conflicts between applications.
- Unresponsive applications: If specific programs are consistently slow, they may need updates or might be incompatible with your system.
Get the best deals on cheap Windows keys and enjoy reliable, genuine software at unbeatable prices!


