Conditional formatting in Excel allows you to visually format cells based on specific conditions or criteria, making it easier to interpret data. When working with dates, conditional formatting can highlight upcoming deadlines, weekends, or past due dates, among other applications. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to conditionally format dates in Excel.
Step 1: Open Microsoft Excel
- Launch Microsoft Excel: Open the Excel application on your computer.
- Open Your Workbook or Create a New One: Click on
Filein the top-left corner, selectOpento choose an existing workbook, or clickNewto create a new workbook.
Step 2: Select the Range of Dates
- Locate the Dates: Navigate to the spreadsheet that contains the dates you wish to format.
- Select the Date Range: Click and drag to select the range of cells that contain your dates.
Step 3: Access Conditional Formatting
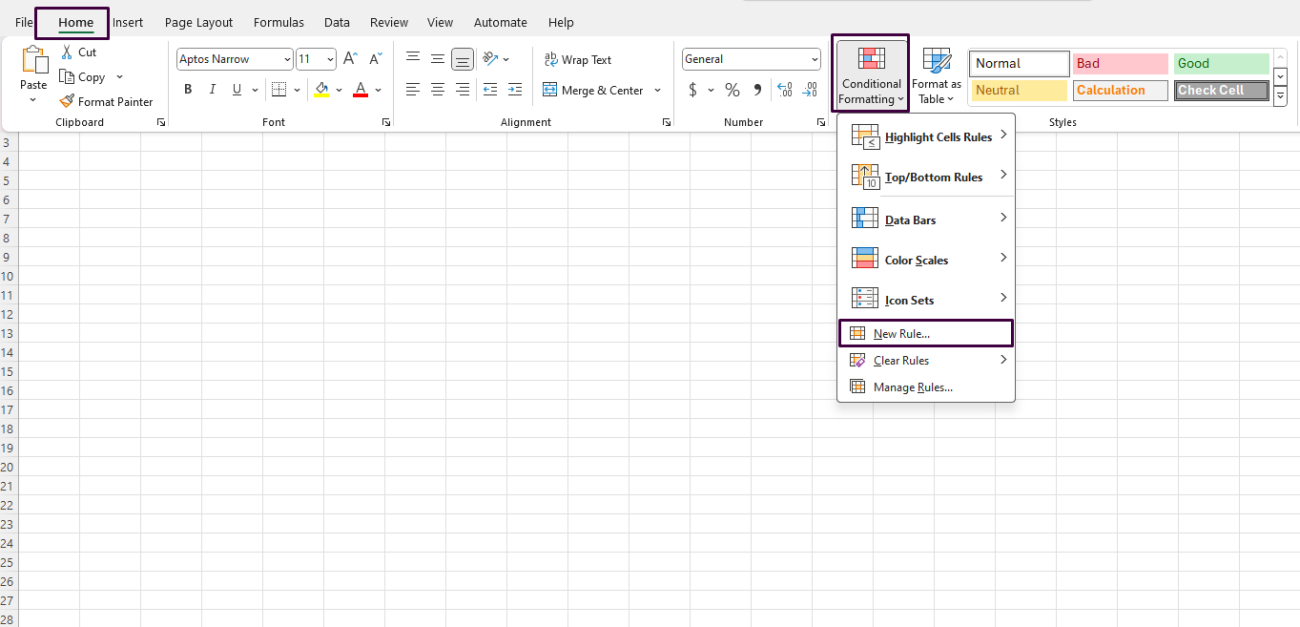
- Go to the Home Tab:
- Click on the
Hometab in the Excel ribbon at the top of the screen.
- Click on the
- Open Conditional Formatting:
- Locate the
Stylesgroup within theHometab. - Click on
Conditional Formattingto open the drop-down menu.
- Locate the
Step 4: Apply Conditional Formatting to Dates
Formatting Based on Date Comparisons
- Select New Rule:
- From the
Conditional Formattingdrop-down menu, click onNew Rule.
- From the
- Choose Rule Type:
- In the
New Formatting Ruledialog box, selectFormat only cells that contain.
- In the
- Set the Formatting Condition:
- Choose
Cell Valuefrom the first drop-down menu. - Choose a comparison operator such as
less than,equal to, orgreater than. - Enter your specific date or use the
TODAY()function for relative comparisons.
- Choose
- Format the Cells:
- Click
Formatto open theFormat Cellsdialog box. - Choose your desired formatting options, such as a fill color or text style, then click
OK.
- Click
- Apply the Rule:
- Click
OKin theNew Formatting Ruledialog box to apply the rule to the selected range.
- Click
Formatting for Specific Conditions
- Highlight Past Dates:
- Follow steps 1–3 from above.
- Use
less thanand=TODAY()to highlight all past dates.
- Highlight Future Dates:
- Follow steps 1–3.
- Use
greater thanand=TODAY()to format future dates.
- Highlight Weekends:
- Select
Use a formula to determine which cells to formatfrom theNew Formatting Ruledialog box. - Enter
=WEEKDAY(A1,2)>5(assuming A1 is the first cell in your range) to identify weekends. - Follow steps 4–5 to apply this rule.
- Select
Step 5: Managing Conditional Formatting Rules
- View and Edit Rules:
- Click
Conditional Formattingin theHometab and selectManage Rules.
- Click
- Edit or Delete Rules:
- In the
Conditional Formatting Rules Manager, select the rule you want to edit or delete. - Click
Edit Ruleto modify orDelete Ruleto remove it from your spreadsheet.
- In the
- Reorder Rules:
- Use the arrow buttons to change the order of rules if necessary, determining which rules take precedence.
Step 6: Save Your Workbook
- Save Your Work: Click on
Fileand selectSaveorSave Asto store your changes.
Looking for a budget-friendly way to get Microsoft Office? Check out our affordable Office keys and save big on premium software!


