Windows 11 introduces features that rely on advanced hardware, such as enhanced security protocols, faster performance, and compatibility with new technologies. To deliver an optimal experience, Microsoft has set a higher bar for hardware specifications compared to previous versions. In this blog post, you can check the Windows 11 System Requirements.
Windows 11 System Requirements
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the minimum hardware requirements for Windows 11:
- Processor:
- Minimum: 1 GHz or faster, with at least two cores.
- Compatibility: Must be a 64-bit processor or system on a chip (SoC).
- RAM:
- Minimum: 4 GB.
- Recommendation: At least 8 GB for smoother multitasking.
- Storage:
- Minimum: 64 GB of available storage.
- Additional: More space may be required for updates and features.
- System Firmware:
- Requirement: UEFI with Secure Boot capability.
- TPM (Trusted Platform Module):
- Version: TPM 2.0.
- Importance: Enhances hardware-level security for features like Windows Hello.
- Graphics Card:
- Requirement: DirectX 12-compatible GPU with a WDDM 2.0 driver.
- Display:
- Minimum: 9-inch diagonal screen size with a resolution of 720p or higher.
- Internet Connection:
- Necessary for initial setup and updates.
- Microsoft Account required for some features.
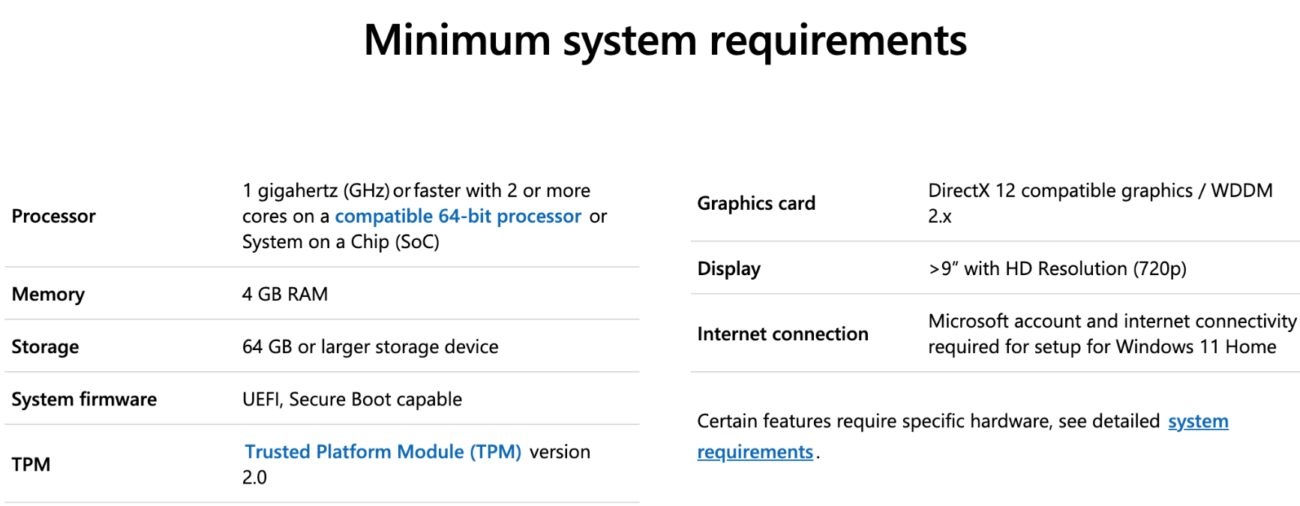
How to Check If Your PC Is Ready for Windows 11
Microsoft offers a handy tool to help users determine if their device is compatible:
- Download the PC Health Check Tool:
- Visit Microsoft’s official website and download the PC Health Check Tool.
- This tool scans your system and provides a compatibility report.
- Check Compatibility Manually:
- Go to Settings > System > About to check your processor, RAM, and system type.
- Confirm if your device supports TPM 2.0 by searching for “tpm.msc” in the Windows search bar.
- Third-Party Tools:
- Applications like WhyNotWin11 provide more detailed insights into compatibility issues.
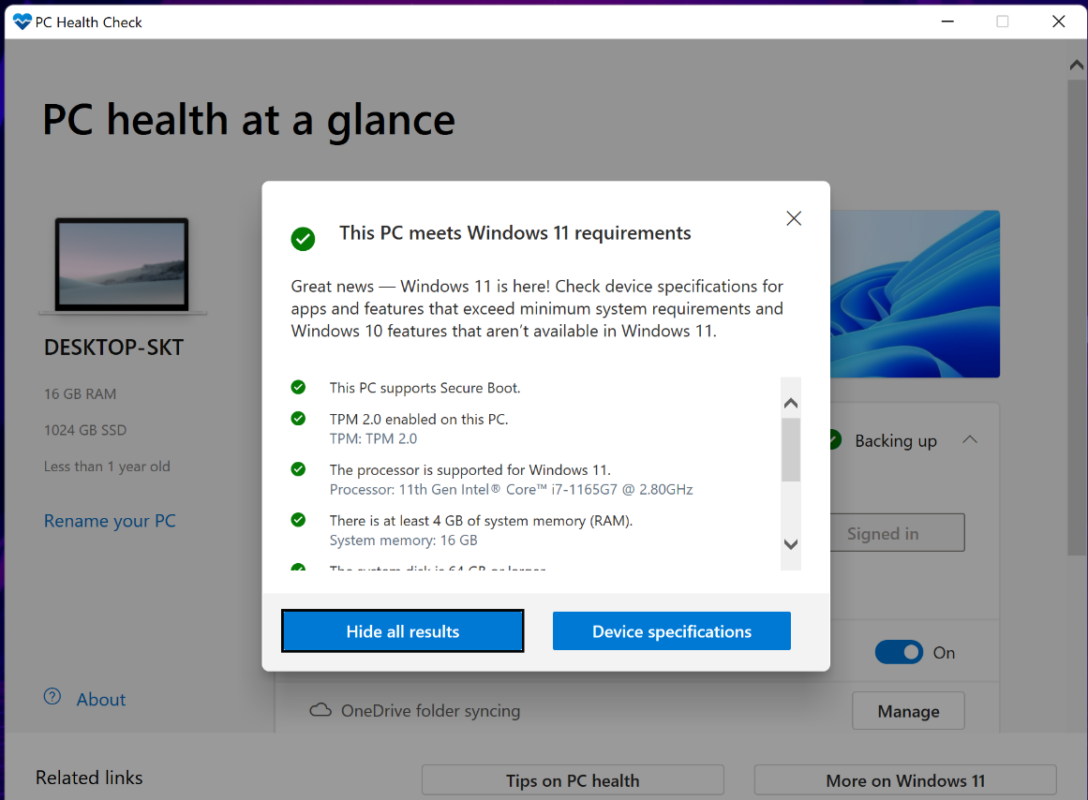
What If Your PC Doesn’t Meet the Requirements?
If your system doesn’t meet the minimum requirements, you have a few options:
- Upgrade Your Hardware:
- Consider upgrading components like RAM, storage, or even your processor if compatible with your motherboard.
- Enable TPM and Secure Boot:
- Many modern PCs have TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot disabled by default. You can enable these features in the BIOS/UEFI settings.
- Stick with Windows 10:
- Windows 10 will continue receiving support until October 2025, giving you time to plan your upgrade.
- Buy a New Device:
- For older PCs, upgrading to a new device with Windows 11 pre-installed might be the most cost-effective option.
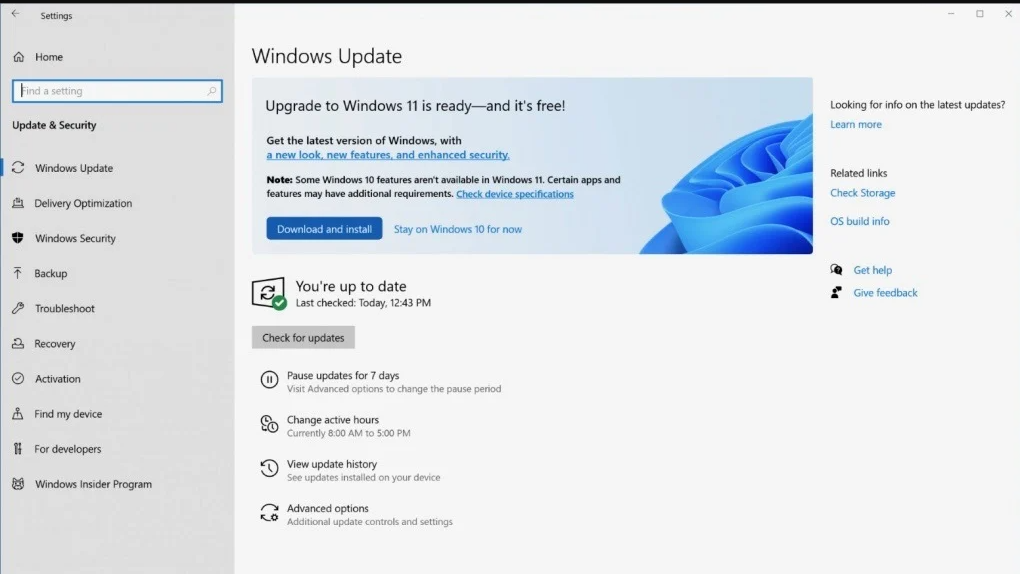
Steps to Upgrade to Windows 11
If your PC meets the system requirements, here’s how you can upgrade:
- Back Up Your Data:
- Use tools like OneDrive or an external hard drive to back up important files.
- Check for Updates:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and see if Windows 11 is offered as an upgrade.
- Download and Install Windows 11:
- If available, follow the on-screen instructions to install Windows 11. The process may take some time, depending on your internet speed and system performance.
- Clean Install (Optional):
- If you prefer a fresh start, you can create a bootable USB drive with the Windows 11 installation media and perform a clean install.
Get the cheapest Windows 11 keys today and unlock the full power of Microsoft’s latest operating system at unbeatable prices!



